The economic relationship between the United States and India is on the cusp of a historic transformation. While headlines scream about trade wars and protectionism, a more nuanced and ambitious story is unfolding between these two democratic giants. Forget the limited trade deals of the past; the US and India are currently negotiating a Bilateral Trade Agreement (BTA) as part of a much broader vision—a vision to double bilateral trade to a staggering $500 billion by 2030.
This isn't just about goods and services; it's about building a comprehensive strategic partnership designed to reshape global supply chains and counterbalance geopolitical rivals. Let's dive deep into the latest developments, the key negotiation points, and the profound strategic implications of this emerging alliance.
The Foundation: From "Chai Pe Charcha" to a Formal COMPACT
The momentum for this new era began in earnest with Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi's visit to Washington D.C. in February 2025. The meeting with President Donald Trump was more than a diplomatic formality; it was a launchpad.
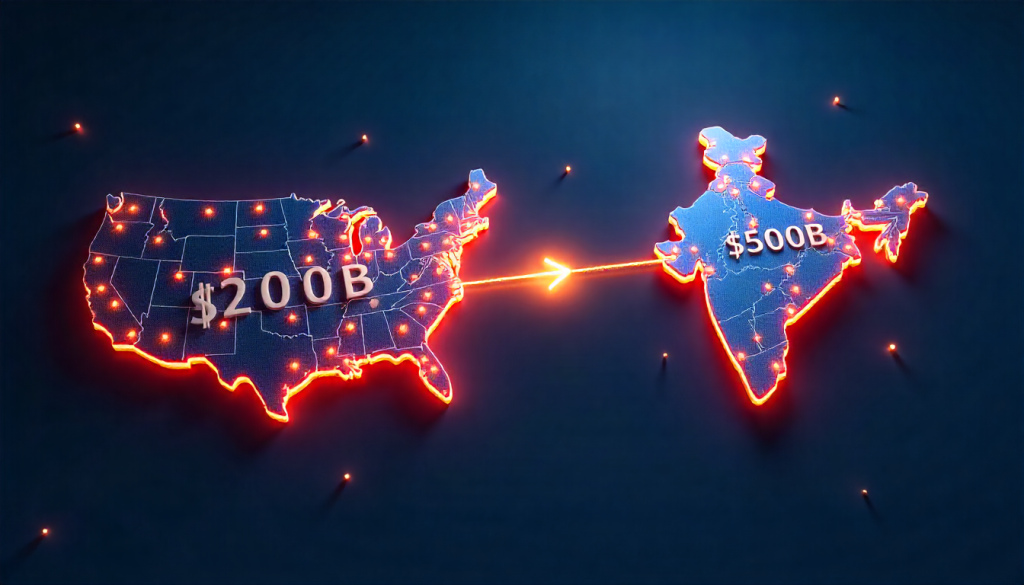
The centerpiece of this new engagement is the U.S.-India COMPACT (Comprehensive Partnership for Global Cooperation and Trade). This framework formally announced the intention to negotiate a significant Bilateral Trade Agreement by the fall of 2025. More importantly, it set an audacious goal: "Mission 500," a target to catapult the trade volume from approximately $200 billion to $500 billion within the next six years.
By April 2025, this vision gained a concrete roadmap with the establishment of the Terms of Reference (ToR), providing a structured path for negotiators. Since then, high-level talks, led on the Indian side by Commerce Minister Piyush Goyal, have been working at a accelerated pace to turn this vision into a reality.
Inside the Negotiation Room: Key Sticky Points
A trade agreement of this magnitude is complex, and both nations are navigating a web of competing interests. The success of the BTA hinges on resolving several critical issues:
1. The Tariff Tango:
The United States has consistently pointed to the disparity in average applied tariffs—India's 17%versus the U.S.'s 3.3%—as a primary barrier. American negotiators are pushing hard for reduced tariffs on a range of exports, including agricultural products (like dairy and poultry), medical devices, and high-tech machinery. The recent U.S. baseline 10% tariff on imports from countries without a specific deal has added a new layer of urgency for India to secure a favorable agreement.
2. The Russian Oil Conundrum:
India's strategic decision to import large volumes of discounted Russian crude oil has been a major point of friction.The U.S. has not shied away from using punitive tariffs to pressure India on this issue. However, recent developments signal a potential shift. Reports indicate that Indian refiners are pausing new orders from Russia and increasing imports of U.S. crude to align with Western sanctions. This goodwill gesture is a crucial confidence-building measure that could smooth the path for the broader trade deal.
3. Market Access and Non-Tariff Barriers:
Beyond simple tariffs,the U.S. is seeking to dismantle non-tariff barriers in India, such as complex regulations, certification requirements, and data localization rules that can hinder American companies in sectors like technology and e-commerce. In return, India has secured improved access for some of its agricultural exports, like mangoes and pomegranates, and will continue to seek easier visa regimes for its skilled professionals.
The Bigger Picture: It's More Than Just Trade
To view these negotiations purely through a trade lens would be a mistake. The BTA is the economic core of a much wider U.S.-India Comprehensive Global Strategic Partnership. This partnership is being fortified simultaneously on two other critical fronts:
· Defense & Security: The two nations are rapidly deepening their defense cooperation. Plans are underway for the co-production of advanced military equipment, such as "Javelin" missiles and "Stryker" armored vehicles, in India. This not only enhances India's military capability but also integrates the two nations' defense industrial bases, reducing dependency on other powers.
· Technology & Supply Chains: Through initiatives like the U.S.-India TRUST, collaboration is accelerating in critical and emerging technologies. Joint efforts in Artificial Intelligence (AI), semiconductor manufacturing, and quantum computing are aimed at building secure and resilient supply chains away from geopolitical competitors.
Conclusion: A Partnership Forging a New World Order
The ongoing US-India trade negotiations represent one of the most significant economic realignments of the decade. While hurdles remain, the political will and strategic necessity on both sides are stronger than ever. The agreement being forged is not a simple transactional pact; it is the economic pillar of a deep-seated alliance aimed at ensuring a free, open, and stable Indo-Pacific.
The success of "Mission 500" and the broader COMPACT will not only redefine the US-India relationship but will also send a powerful message about the shape of global trade and geopolitics in the 21st century. The world is watching as two great democracies build a partnership destined to shape the future.






Leave a Reply